Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 , He
, He
 , C
, C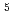
 and Ne
and Ne
 ions
ionsIwamatsu, Kazuhiro; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kimura, Atsushi; Kurashima, Satoshi; Katsumura, Yosuke
no journal, ,
Heavy ion beams, one of the high linear energy transfer (LET) radiations induce specific irradiation effects which are different from those of low LET radiations. The effects are attributed to heterogeneous distribution of reactive species along their trajectories, so called "track structure". Water was selected as target in this study because more data exist for radiolysis than any other substances. Hydroxyl radical (OH), one of the most important water decomposition species, was focused on by using bromide ion as a probing reagent, and their reactions were observed by the ion beam pulse radiolysis system. The formation and decay of Br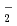 were observed at 375 nm (
were observed at 375 nm ( [Br
[Br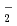 ] = 9000 M
] = 9000 M
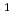 cm
cm
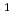 ). The formation chemical yield of it after pulse irradiation decreased with increasing atomic numbers of the incident ions. Radical recombination reaction occurs easier by higher LET ions because of denser radical formations. Therefore, the decrease in the yields of OH scavenged by Br
). The formation chemical yield of it after pulse irradiation decreased with increasing atomic numbers of the incident ions. Radical recombination reaction occurs easier by higher LET ions because of denser radical formations. Therefore, the decrease in the yields of OH scavenged by Br induces the decrease in the chemical yields of Br
induces the decrease in the chemical yields of Br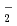 . The decay rates of the chemical yields increased with the atomic mass of the ions. The concentrations depend on the dose rate and chemical yield, and the dose rates proportional to LET value. The concentrations after pulse increased with increase in the atomic mass of the ions and resulted in faster decay in heavier ions.
. The decay rates of the chemical yields increased with the atomic mass of the ions. The concentrations depend on the dose rate and chemical yield, and the dose rates proportional to LET value. The concentrations after pulse increased with increase in the atomic mass of the ions and resulted in faster decay in heavier ions.
 -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationKumagai, Yuta
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kai, Takeshi; Yokoya, Akinari; Ukai, Masatoshi*; Watanabe, Ritsuko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hata, Kuniki; Matsuyama, Taichi*; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Muroya, Yusa*; Katsumura, Yosuke*; Tsukada, Takashi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hirade, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
Positronium (Ps; a bound state of positron and electron) has a negative work function in materials and forms a bubble state in liquids. On the way of stable bubble state, the bubble grows and probably oscillates. The usual fast bubble formation has not been observed with the time resolution of the positron annihilation methods that is usually 100-200 pico-seconds. There had been many anomalous phenomena observed in the room temperature ionic liquids (RTIL). Recently it was found that very slow bubble formation caused these anomalous phenomena. And hence the oscillation of the Ps bubble was successfully observed by the change of the annihilation rate of the triplet Ps that is affected by the size of the bubble. The oscillation and the decay of the bubble give the information of the viscoelastic properties at the sub-nano scale. The temperature dependence of the oscillation has been also successfully indicated.
Hiroki, Akihiro; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
Polymer gel dosimeters consisting of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate, and tetrakis (hydroxymethyl) phosphoniumu chloride with radiation-crosslinked hydroxypropyl cellulose gel were prepared. The prepared dosimeters were irradiated with 150 MeV/u He ions, 290 MeV/u C ions, and 500 MeV/u Fe ions at HIMAC, in which a linear energy transfer (LET) of He, C, and Fe ions were 2.2, 13, and 182 eV/nm, respectively. Absorbance of the irradiated dosimeters increased with an increase in the dose up to 10 Gy. The absorbance at total doses of 5 Gy decreased with increasing dose rate in all of the heavy ions. The dosimeter irradiated with Fe ions exhibited the lowest absorbance in these samples. It was found that the absorbance decreased with increasing dose rate as well as LET of the heavy ions.
Kimura, Atsushi; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
Large quantities of polysaccharides are produced on earth. The polysaccarides possess unique structures, distinctive properties, and are non-toxic and biodegradable. Ionizing radiations are widely used convenient tool for modifying of the polysaccharides by decomposition, grafting, and cross-linking techniques. Until now, radiation cross-linked materials have only been produced either from polysaccharide derivatives or using cross-linking reagents because natural polysaccharides have poor solubility in water and organic solvents and low chemical reactivity. Radiation modifications of cellulose in RTILs were carried out to obtain its gel material under humid condition, and dependence of the yields of the gels was investigated on water content.
Chen, J.; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari
no journal, ,
Electrodialysis is a green technology for separation of ionic species from aqueous solution and has been used in preparation of drinking water and treatment of waste water. Polymer electrolyte membranes are the most important components in the electrodialysis systems. In this study, we use the radiation grafting technology to preparate the cation and anion exchange membranes. It was found that the ion exchange capacity (IEC) increases with increasing degree of grafting, and the conductivity increases with increasing IEC. However, the conductivity for cation-type membranes is several times higher than for anion-type membranes at the same level of IEC. The cation and anion exchange membranes were tested using a simple electrodialysis cell, in which the maximum percent removal of the cesium ions can be closely reached to 100% using the prepared polymer electrolyte membranes with low IEC.
Seguchi, Tadao*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Shimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki
no journal, ,
The degradation of ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) as the cable insulation material for nuclear power plants (NPP) was studied by the accelerated thermal ageing, radiation ageing and thermal - radiation combined ageing. The oxidation of EPR proceeded with both thermal and radiation and the decay of mechanical property was closely related to the degree of oxidation. The thermal oxidation was much affected by the content of antioxidant in EPR as a stabilizer, that is, the oxidation rate was almost same above a critical content of antioxidant but increased much by the decay less than the critical value. On the other hand, the radiation oxidation rate was scarcely affected by the content of antioxidant. As the antioxidant in EPR evaporates from the material surface during thermal ageing and decomposes with dose by the radiation ageing, so the oxidation distribution in the depth of EPR sheet specimen was changed with reflecting the content of antioxidant above or less than the critical value. In the case of combined oxidation of thermal and radiation ageing, the yield and distribution of oxidation in EPR specimen were different by the sequence of ageing combination. The mechanical properties were well reflected by the yield and distribution of oxidation products. As far as the antioxidant content was held above the critical value, the degradation was almost same among the sequence of thermal and radiation ageing, but when the antioxidant was decayed less than the critical value the degradation was much increased in the reverse sequential ageing. For the qualification testing method of the NPP cables, the reverse sequential combination, radiation then thermal ageing, could be recommended.
Izumi, Yudai; Yamamoto, Satoshi*; Fujii, Kentaro; Yokoya, Akinari
no journal, ,
Fujii, Kentaro; Izumi, Yudai; Narita, Ayumi; Yokoya, Akinari; Herv du Penhoat, M.-A.*; Ghose, K.*; Vuilleumier, R.*; Gaigeot, M.-P.*; Politis, M.-F.*
du Penhoat, M.-A.*; Ghose, K.*; Vuilleumier, R.*; Gaigeot, M.-P.*; Politis, M.-F.*
no journal, ,
In order to reveal a role of hydration water on the destruction of dR molecule induced by core electron ionization, we measured a mass spectrum of desorbed ions from the hydrated dR film exposed to soft X-rays with energy above oxygen K-shell ionization threshold (560 eV). The spectral changes of X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) of the films after the soft X-ray exposures were also examined the chemical structure of the irradiation products. The yield of the desorbed ions, which were produced by the destruction of furanose ring structure, obviously decreased with depositing one layer of water molecules on the film. This result suggests that the hydration water layer on dR film suppresses an intense destruction of the furanose ring structure of dR induced by the core ionization, or the desorption of the resulting fragment ions from the sample film. We also observed new peaks emerging around 534-536 eV in the XANES spectrum of the hydrated sample irradiated. These new peaks are located at the similar energies to those of XANES peaks of formic acid. The hydration water could also contribute to produce the newly forming products containing a carboxyl group.
Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Kimura, Atsushi; Hiroki, Akihiro; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
Sodium carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) is a water-soluble polysaccharide derivative so that has been widely used in many commercial applications such as food, medicine and cosmetic fields. The ionizing radiation generally leads CMC degradation in diluted aqueous solution. CMC hydrogels, however, are produced by using ionizing radiation processing in the paste-like conditions, i.e. concentration at 10-60%. The mechanism of crosslinking reaction in CMC is yet not known. It is assumed that this reaction is greatly involved the impact of the distance between molecular chains and the entanglement of molecular chains in this specific condition. Since the CMC is a polyelectrolyte and form a complex with metal salts in solution, it hit on an idea to control the size of those complexes by changing the electric charges on CMC macromolecule chains with metal ions. We investigated gelation behavior by adding high concentrated metal ions to CMC solution before irradiation. Formation of gels in the CMC / salt solutions was observed by a dynamic viscoelasticity analyzer. For 5% CMC with any salts during irradiation up to 10 kGy, the storage modulus [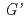 ] of the sample solution increased with concentration of metal ions and dose in the lower frequency range [0.1-1.0 rad/s]. Increase in the
] of the sample solution increased with concentration of metal ions and dose in the lower frequency range [0.1-1.0 rad/s]. Increase in the 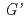 value means gelation of CMC. Metal ions make reduce interaction of the charge for CMC macromolecule chains in the solution. It is considered that crosslinking reaction easily occurs as compared without the salt, because the distance between CMC macromolecule chains becomes closer.
value means gelation of CMC. Metal ions make reduce interaction of the charge for CMC macromolecule chains in the solution. It is considered that crosslinking reaction easily occurs as compared without the salt, because the distance between CMC macromolecule chains becomes closer.
 -ray-induced grafting
-ray-induced graftingNuryanthi, N.*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Kitamura, Akane; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yoshimura, Kimio; Sawada, Shinichi; Hasegawa, Shin; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Suzuki, Akihiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
The ion-track grafting of a vinylbenzyl chloride (VBC) into a poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) film is necessary for preparing nanostructured hydroxide-ion conductive electrolyte membranes. A key for success here is to obtain as high graft levels as possible (for higher conductivity) in a smaller number of tracks (for improving the other membrane properties). To this end, therefore, the effect of the medium for the VBC grafting was investigated as part of our continuing effort to optimize the experimental conditions. A 25  m-thick ETFE film was irradiated in a vacuum chamber with 560 MeV
m-thick ETFE film was irradiated in a vacuum chamber with 560 MeV  Xe at different fluences, and then the grafting was performed by immersing the irradiated films in a 20vol% VBC monomer at 60
Xe at different fluences, and then the grafting was performed by immersing the irradiated films in a 20vol% VBC monomer at 60 C. A medium was a mixture of water (H
C. A medium was a mixture of water (H O) and isopropyl alcohol (iPrOH) at different volume ratios. The degree of grafting increased as the H
O) and isopropyl alcohol (iPrOH) at different volume ratios. The degree of grafting increased as the H O content became higher, and reached a maximum in pure H
O content became higher, and reached a maximum in pure H O.
O.
Saiki, Seiichi; Shibata, Takuya; Hoshina, Hiroyuki; Ueki, Yuji; Kasai, Noboru; Seko, Noriaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Maekawa, Yasunari
no journal, ,